2.1 Trailblazer Documentation
About
Trailblazer is a collection of gems to help you structure growing Ruby applications. It does so by providing a higher level of architecture through new abstractions.
Abstractions
The layers we provide are designed to be stand-alone and do not require you buying the full TRB stack.
- Form objects to move validation and processing logic out of models into dedicated and renderable objects. → REFORM docs
- Service objects that embrace your business code, orchestrate different domain layers, and allow for a solid, testable architecture. → OPERATION docs
- View components for better encapsulation in your HTML views. → CELLS docs
- Representers to parse incoming JSON or XML documents, and to serialize outgoing data. → REPRESENTABLE docs
- Trailblazer does not come with SQL abstractions or routing as those layers are provided by exisiting frameworks such as Rails or Hanami.
Are you new to TRB? Then it’s probably best to start with our LEARN section and find out more about this framework!
Currently, the framework consists of around 40 gems. The main gem trailblazer is an umbrella gem with the sole reason to pull all default dependencies for you. Feel free to pick and choose what you need for your applications.
Our mission
Trailblazer empowers developers to build better applications. By “better” we mean maintainable, stable and, yes, fun to work with!
Our approach enforces encapsulation by providing new abstraction layers. It maximizes testability and reusability, and simplifies onboarding of new developers as we have strong conventions, thorough docs and screencasts, and a vivid community.
Unlike other “modern architecture” approaches in the Ruby community (as seen in numerous blog posts and books) neither do we tell you how to apply a new, fancy design pattern in your project by giving you suggestions for vague “best practices”, nor do we instruct how to introduce that new, self-tailored service object. No. we give you battle-tested functions, abstractions and classes that enforce a clean architecture.
We firmly believe that the utilization of ready-to-use layers will always prevail over a documentation-driven approach. In the latter, reliance on constantly outdated “architecture docs” creates a continuous struggle for a designated senior to document the process of creating a specific type of object.
Learn
Believe it or not, but you can learn about Trailblazer step-wise! It’s usually smart to start checking out operations, then form gems using Reform, and after that macros and Rails integration.
Trailblazer Tales
For a while we’ve been pushing very short 5-min videos teaching you how operations work, what testing looks like and which features they bring for your daily development.
Producing those instructional screencasts turned out to be a lot of fun (and a bit of work), so expect a new episode every few weeks. This is definitely much simpler than writing books!
Grab a coffee and watch the first few episodes to quickly grasp how to master this indispensable tool to structure your business logic.
Books
The Trailblazer - A new architecture for Rails book from 2017 is very outdated and discusses Trailblazer 1.x! However, the first two chapters are worth a read, if you want to pick up the spirit.
It’s free to download.
The Building your own authentication library with Trailblazer book, however, is up-to-date. It’s missing part II which discusses Rails integration, but gives you a nice tour through operations.
Everything discussed in the “Buildalib” book is also covered in our videos.
Tutorials
Here’s the link to the “Rails Basics” tutorial.
We are revisiting our tutorial section in 2024.
2.1 Migration
Call API
Call API Operation.call
In versions before 2.1, the automatic merging of the params part and the additional options was confusing many new users and an unnecessary step.
# old style
result = Memo::Create.( params, "current_user" => current_user )The first argument (params) was merged into the second argument using the key “params”. You now pass one hash to call and hence do the merging yourself.
# new style
result = Memo::Create.( params: params, current_user: current_user )The new call API is much more consistent and takes away another thing we kept explaining to new users - an indicator for a flawed API.
For a soft deprecation, do this in an initializer:
require "trailblazer/deprecation/call"You will get a bunch of warnings, so fix all Operation.() calls and remove the require again. This is provied by trailblazer-future gem.
Call API Step Signature
In case your steps expose a signature as follows, you’re safe.
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
step :create_model
def create_model(options, params:, **)
# ..
end
endBy convention, we renamed option to ctx, but it is completely up to you to adopt this.
Nevertheless, the “old style” signatures won’t work anymore.
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
def create_model(options)
# ..
end
# or
def create_model(model:, **)
# ..
end
endNeither a single options nor keyword-arguments-only are gonna fly as the new step signature is more restrictive and always requires you to maintain the ctx (or options, if you will) as the first positional argument, then keyword arguments.
Double splat operator ** at the end will be required to in order to discard unused kw args.
You can introduce this change before actual migration to 2.1.
Call API pass/fail
Steps declared as success or failure are now renamed to pass and fail respectively.
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
success :model
failure :handle_some_error
endChange it as follows.
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
pass :model
fail :handle_some_error
endIf you are using Rubocop it will probably start complaining about unreachable code because it just so happens that fail is also a Ruby Kernel’s method. One solution to this could be to add a custom rule to .rubocop.yml like this:
Lint/UnreachableCode:
Exclude:
- '*/**/concepts/**/operation/**/*'
Style/SignalException:
Exclude:
- '*/**/concepts/**/operation/**/*'There is also a trick that will allow you to do this rename before actually migrating to 2.1. You can put this in an initializer:
Trailblazer::Operation::Pipetree::DSL.send(:alias_method, :pass, :success)
Trailblazer::Operation::Pipetree::DSL.send(:alias_method, :fail, :failure)This way you could introduce this change before actual migration to 2.1. Just don’t forget to remove it after updating gems to 2.1.
Call API pass_fast/fail_fail
Now every step that may end up in pass_fast or fail_fast signals need an extra option that indicates fast track usage. Change this operation:
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
step :create
def create(ctx, **)
Railway.pass_fast! if ctx[:model].save
end
endUse the :fast_track option to let Trailblazer know about the potential new signal being emitted.
class Memo::Create < Trailblazer::Operation
step :create, fast_track: true # notice the extra option :fast_track
def create(ctx, **)
Railway.pass_fast! if ctx[:model].save
end
endContext
The keys for ctx used to be mixed up, some where "longer.strings", some were :symbols. The new context implementation Context::IndifferentAccess now allows to use both.
ctx["model"]
ctx[:model] # => same!This also works for namespaced keys, which you still might find helpful.
ctx["contract.default"]
ctx[:"contract.default"] # => same!On the core level, we use symbol keys, only (e.g. :"contract.default").
The default implementation of the context object can be set by overriding Context.implementation. For example, if you want the old behavior back.
class Trailblazer::Context
def self.implementation
Context # old behavior.
end
endNote that the override might be deprecated in favor of a dependency injection.
Nested
The Nested macro allows to, well, nest activities or operations, providing a neat way to encapsulate and reuse logic.
Nested Deprecation
In 2.1, the [Subprocess macro] is the standard way for nesting. The Nested macro should only be used when you use the dynamic version where the nested operation is computed at runtime using :builder.
An exception will warn you about the inappropriate usage.
[Trailblazer] Using the `Nested()` macro with operations and activities is deprecated. Replace `Nested(Create)` with `Subprocess(Create)`.Nested input and output
Both the :input and :output options that used to go with Nested(Present, :input: ...) are now a generic option in Trailblazer. Move them behind the
macro parenthesis.
# 2.0
Nested(Present, input: :my_input, output: :my_output)
# 2.1
Nested(Present), input: :my_input, output: :my_outputAn exception will stop compilation if you fail to obey.
ArgumentError: unknown keyword: inputBehold of another tiny API change! The :output filter signature has changed for a better.
In Trailblazer 2.0, the following signature was allowed.
# 2.0
Nested(Present,
output: ->(ctx, mutable_data:, **) {
{model: mutable_data[:article]} # you used the {mutable_data} keyword argument.
}
)Mind the arguments being passed to :output. The first positional is the original outer context, the context from the nested operation comes as a mutable_data: keyword argument.
In 2.1, those two have swapped.
# 2.1
Nested(Present),
output: ->(inner_ctx, article:, **) {
# {inner_ctx} is {mutable_data}
{model: article} # you used the {mutable_data} keyword argument.
}The inner context from the nested operation comes first, as a positional argument. Note how you can conveniently use keyword arguments to access variables from this inner ctx (e.g. article:). Keep in mind, the naming is completely up to you. We use inner_ctx/ctx and original_ctx in our code.
If you also need the original context in the :output filter, use the :output_with_outer_ctx option.
# 2.1
Nested(Present),
output_with_outer_ctx: true
output: ->(inner_ctx, original_ctx, article:, **) {
{
model: article,
errors: original_ctx[:errors].merge(inner_ctx[:errors]) # you can access the outer ctx!
}
}The original, outer ctx comes in as a second positional argument.
You do not need to extend Uber::Callable in classes with #call methods anymore.
Check the Variable Mapping docs for a complete explanation.
Nested Fast Track
Don’t forget to declare fast track usage if you expect it from within nested operation, like this:
Nested(Present), input: :my_input, output: :my_output, fast_track: trueAnother difference is that in 2.0, when you were using pass_fast in nested operations, it would stop only the nested operation from executing. After this the outer one would continue executing.
Now returning pass_fast in nested operation will stop both, inner and outer operation with success as a final result. If you rely on old behaviour you can still have it with proper signals mapping:
Nested(Present), input: :my_input,
output: :my_output,
fast_track: true,
Output(:pass_fast) => Track(:success), # pass_fast now mapped to `just` a success
Output(:fail_fast) => End(:failure)Macro API
Macros are functions that add a task along with specific options to the activity. In TRB 2.0, those (historically camel-cased) functions returned an array with two elements.
module MyMacro
def self.NormalizeParams(name: :myparams, merge_hash: {})
task = ->((ctx, flow_options), _) do
ctx[name] = ctx[:params].merge(merge_hash)
return Trailblazer::Activity::Right, [ctx, flow_options]
end
[task, name: name] # old API
end
endIn 2.1, a hash is returned. Note that :name is :id now.
module MyMacro
def self.NormalizeParams(name: :myparams, merge_hash: {})
task = ->(ctx, flow_options, _) do
ctx[name] = ctx[:params].merge(merge_hash)
return ctx, flow_options, Trailblazer::Activity::Right
end
# new API
{
task: task,
id: name
}
end
end
This allows for a much richer macro experience where you might add additional steps via a macro, use DSL options such as :before and :after and add taskWrap extensions. [macro API]
A common error if you don’t return a hash from your macro is a call on Array.
NoMethodError:
undefined method `call' for #<Array:0x000055663116be98>
# gems/trailblazer-context-0.4.0/lib/trailblazer/option.rb:9:in `call!'Macro API Signature and Return
In Trailblazer 2.0, macros were automatically using the task interface. Mind the arguments and the return value.
task = ->(ctx, current_user:, model:, **) {
# do something
# return true/false
}In Trailblazer 2.1, macros use the circuit interface per default. If you want the simpler task interface, you need to wrap your task using Binary().
def MyMacro()
task = ->(ctx, current_user:, model:, **) {
# do something
# return true/false
}
{
task: Trailblazer::Activity::TaskBuilder.Binary(task), # wrap the callable.
id: "my_macro"
}A common error if you don’t wrap your macro is an ArgumentError.
ArgumentError:
missing keywords: current_user, modelMacro API Step id
In case you used the same macro twice in one operation, like this for example:
class Create < Trailblazer::Operation
step Contract::Persist(method: :sync)
step Contract::Persist(method: :save!)
endYou will have to specify id explictly for one of them:
class Create < Trailblazer::Operation
step Contract::Persist(method: :sync)
step Contract::Persist(method: :save!), id: "some_custom_unique_id"
endContract DSL
It was possible to define contracts on the operation level using a DSL.
class Create < Trailblazer::Operation
contract do
property :id
end
step Contract::Build()
step Contract::Validate()
endSince the usability doesn’t outweigh the complexity needed to implement such DSL, we decided to remove that functionality for now.
Instead, use an explicit inline class and the :constant option.
class Create < Trailblazer::Operation
class Form < Reform::Form
property :id
end
step Contract::Build(constant: Form)
step Contract::Validate()
endTrailblazer loader
Usage of a trailblazer-loader is now discouraged as it’s slower than the ones provided by Rails and it’s error prone.
In short, we decided to adopt the Rails naming scheme and change operation names from User::Create to User::Operation::Create, so the file name and class path are in sync.
Read the details here.
We highly recommend changing this with your upgrade as it highly improves the dev experience.
Developer
Trailblazer provides a rich set of developer tools to ease debugging and make modelling processes a pleasant experience.
The developer gem contains tools to help you visualize and debug Trailblazer code. Its development features such as tracing or exception handling are advanced tools and will become your best friends very quickly.
Constant
We advise you to alias the Developer constant to something handy, such as ::Dev in your project. For instance, in Rails you’d have the following line in a config/initializers/trailblazer.rb initializer.
# config/initializers/trailblazer.rb
require "trailblazer/developer"
Dev = Trailblazer::Developer
Wtf?
The iconic wtf? method is one way to invoke an operation with tracing turned on. During the execution, invoked steps are traced and printed in the console as a tree-view, helping you to understand the code path the operation took. It is one of Trailblazer’s most-loved features and was introduced in Trailblazer 2.1.
When working with a Trailblazer::Operation simply invoke its #wtf? method.
result = Memo::Operation::Create.wtf?(params: {title: "Remember me..."})
On the console, you can see the printed trace in all its beauty.
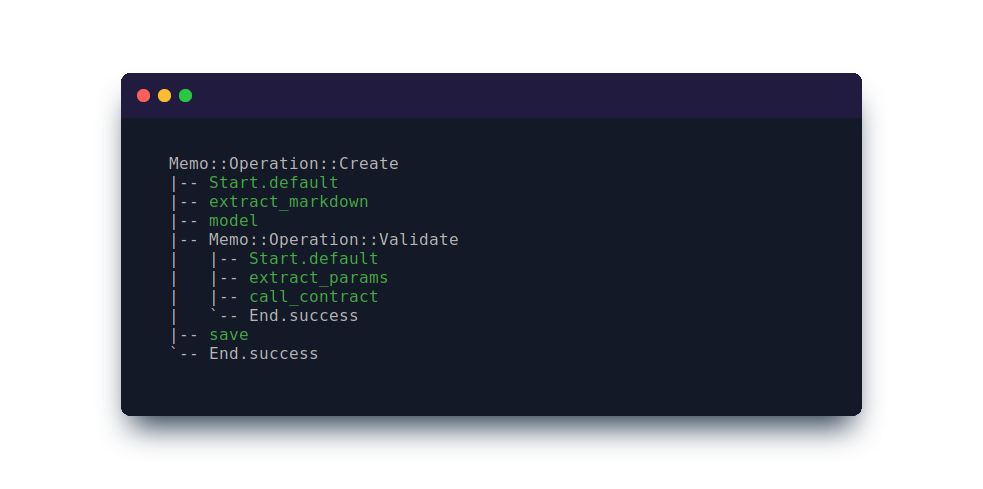
This method is especially helpful if you want to
- Debug an exception happening somewhere deep in your code.
- Find out which step changed the track to failure.
- Focus on specific step(s) to find out what
ctxmutations are happening inside them.
Wtf? Exception
In case of an exception somewhere in the operation or its nested activities, wtf? will print the trace path to the closest point where the exception was thrown.
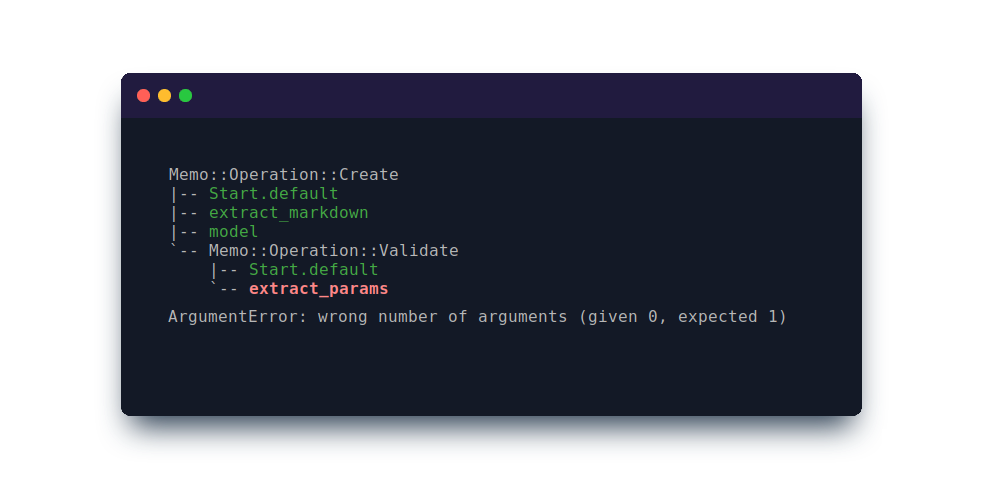
The original exception will be visible on the console, too.
Please note that this is a higher-level debugging tool that does not confront you with a 200-lines stack trace the way Ruby does it, but pinpoints the exceptional code and locates the problem on a task level.
This is possible due to you structuring code into higher abstractions, tasks and activities.
Wtf? Activity
The #wtf? class method is only available for Trailblazer::Operation subclasses. You will get an exception if you try to use it with Trailblazer::Activity::Railway and other activities.
NoMethodError: undefined method `wtf?' for Memo::Operation::Create:ClassHowever, tracing can be used with low-level Activity classes, too.
module Memo::Operation
class Create < Trailblazer::Activity::Railway # Note that this is not an {Operation}!
step :extract_markdown
step :model
# ...
end
end
You have to use the clumsier Developer.wtf? method for tracing.
ctx, _, signal = Trailblazer::Developer.wtf?(
Memo::Operation::Create, [{params: {title: "Remember me.."}}, {}]
)
As always with Activity subclasses, it operates with the circuit interface.
Wtf? color_map
The color_map option allows you to customize default coloring scheme being used to render passed or failed steps.
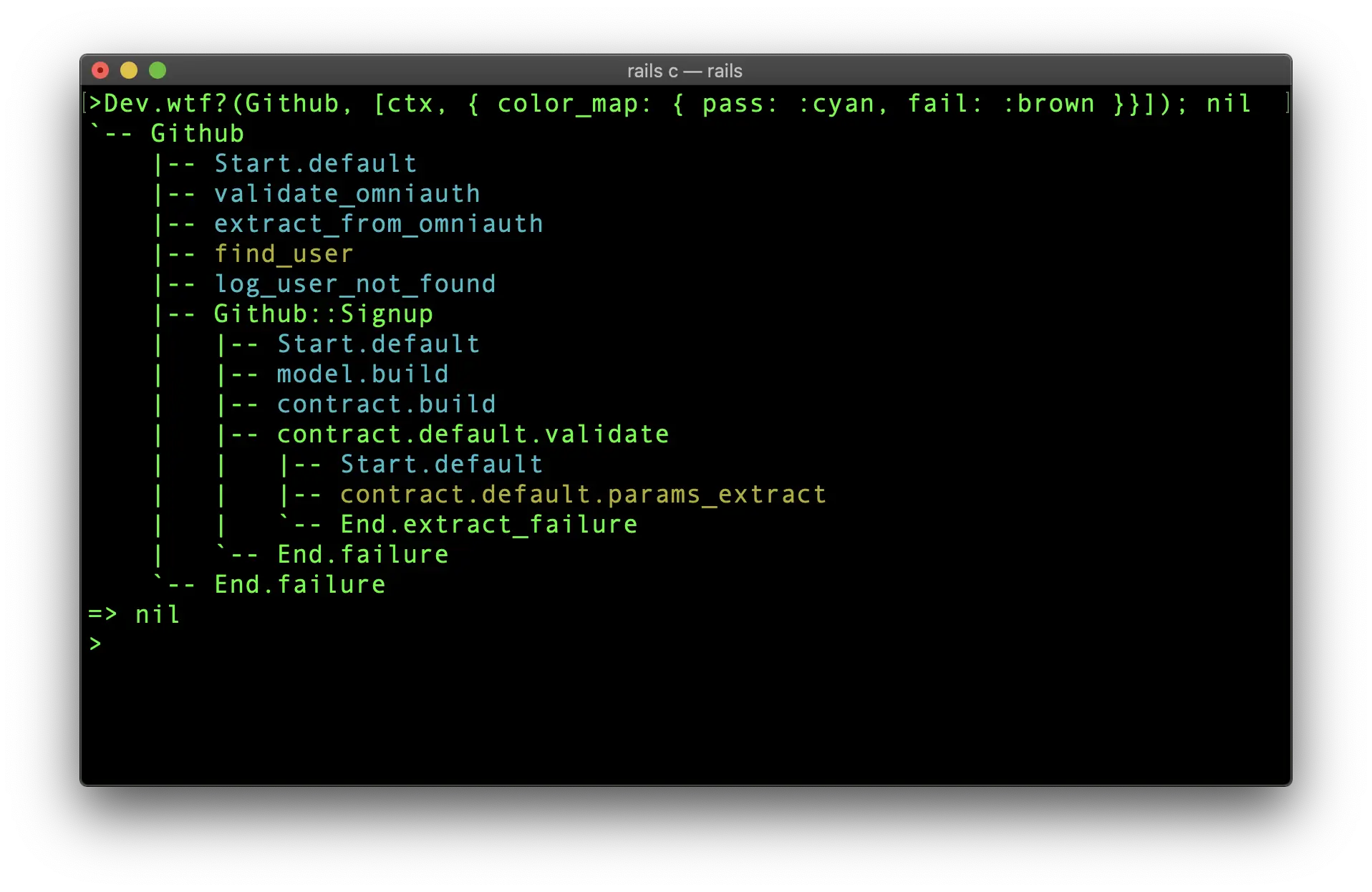
Render
It often is helpful to visualize an activity. One way is the render helper.
puts Trailblazer::Developer.render(Memo::Create)The rendered output prints each task, its outputs and where they’re connected to.
We’re working on improved visualization for the console, and for the web editor. If you want to help, please ping us on our chat.
Render Linear
Client
The Developer::Client module provides functions to work with activities and workflows created in the PRO editor.
Client Import
Notes
- IDs are extracted from the label of the element. They get
chomped to remove a potential newline at the end and reduce confusion. - It is currently not possible to assign semantics to arrows via the label. In the meantime, use the
:queryoption. # TODO
Graph
With trailblazer-activity 0.16.0, the Introspect::Graph API has been moved to trailblazer-developer and might get replaced. Please refer to the Introspect::Nodes API.
To find out the structure and composition details about any activity, use the Introspect API.
Graph Find
You may use Graph#find with a block for a more complex search.
node = graph.find { |node| node.task.class == Trailblazer::Activity::Circuit::Step::Binary }
Alternatively, using the Graph#find method with an ID provided, you can retrieve a particular node in the activity’s circuit.
Consider the following activity.
class Memo::Update < Trailblazer::Activity::Railway
step :find_model
step :validate, Output(:failure) => End(:validation_error)
step :save
fail :log_error
end
You can introspect a certain element by using find(id).
graph = Trailblazer::Developer::Introspect.Graph(Memo::Update)
node = graph.find(:validate)
Note that all queries go via a Graph instance.
Graph Node API
The returned node instance exposes several inspect helpers.
The ID of the element is retrieved by using #id.
# puts node.id.inspect #=> :validate
To see what actual task sits behind this circuit’s node, use #task. This is always the low-level task that responds to a circuit interface. It might be a wrapper around your actual logic, provided by the DSL.
# puts node.task #=> #Trailblazer::Activity::TaskBuilder::Task user_proc=validate>
Outgoing connections from a task can be queried using #outgoings. This returns an array of all outgoing arrows.
# left, right = node.outgoings # returns array
Graph Outgoing
An Outgoing provides several interesting fields.
You can retrieve the connected element by using #task. It returns the actual low-level task.
# puts left.task #=> #Trailblazer::Activity::End semantic=:validation_error>
The #output method returns the Output instance that connects the task to the next element.
# puts left.output.signal #=> Trailblazer::Activity::Left
# puts left.output.semantic #=> :failure
The Output#signal field returns the signal object the task returns to trigger that connection. To see the semantic of this output, use Output#semantic.
Graph Outputs
The Node#outputs method returns an array of Output objects defining each output of outgoing connections of a specific node.
outputs = node.outputs
left = outputs[0] #=> output object


